The History of Sound Design
Although the term “sound design” has been around for nearly four decades–and the practice has been pursued much longer–its use has only recently become nearly ubiquitous. A day cannot go by that I do not see #sounddesign appended onto the end of a multitude of tweets from around the world. We now have the invaluable website DesigningSound.org, which distributes information about our community’s adventures, musings, and technical inquiries. And our Boom Box Post blog often touts titles such as Creature Speech Sound Design Challenge or Smoke and Mirrors: Unexpected Sound Design Sources.
Why this sudden renaissance of the term “sound design”? This week, I decided to take a closer look at the history of the term, the differences in how it is used across the film and television, interactive and immersive media, and theater industries, and its use and abuse.
Sound Design: A History
The term “sound designer” was used for the first time in film in 1979. Francis Ford Coppola granted Walter Murch the title of Sound Designer for his work on Apocalypse Now, marking the first use of the term as a credit in film. Until that point in time, the usual credit, Supervising Sound Editor or Sound Editor, was generally accepted as a purely technical role on a film crew. Coppola felt that this new title encompassed his feeling that Murch had been a key creative team member who added to the artistry and overall creative intention of the film. It was also to be understood that Murch oversaw the overall sound concept of the film, including dialogue, sound effects, foley, and the final mix, just as a supervising sound editor would normally do.
Walter Murch’s creative storytelling through sound and his integration into the Apocalypse Now team as early as pre-production surely earned him this extra accolade. I would love to wax poetic about the sound of Apocalypse Now, but that certainly deserves its very own blog post. Instead, please read this interview with Murch himself regarding the sound of the film.
Surely, the sound design on Apocalypse Now was of the highest quality and extremely innovative for its time. However, it is important to note that this was not the first time that an inventive sound editor played a critical role in a film’s sound. Instead, this was the first time that the title Sound Designer was used to describe that work, thereby expressing the beginning of a shift in the industry’s attitude toward sound editorial. The same job would have previously been listed as Supervising Sound Editor or Re-Recording Mixer. Case in point: we can all agree that Ben Burtt’s work in Star Wars: Episode IV – A New Hope, released in 1977, was sound design. Afterall, he designed the sound of the lightsaber! Yet, he was originally credited with Special Dialogue and Sound Effects. In the 1997 and 2004 re-released editions, his credit was changed to Sound Designer.
Sound Design Across Industries
One of the aspects that makes the title Sound Designer so interesting is that it is not controlled by any labor unions or industry organizations except in the arena of theater. So, unlike many other roles which have been established and then held to the same set of standards over the years, the idea of what makes someone a sound designer is free to evolve. Thus, every industry has taken this idea and slowly crafted a meaning that fits its own needs, resulting in a varied and sometimes confusing use of the term.
Film & Television
In the television and film industry, the Motion Picture Editor’s Guild, MPEG (local IATSE chapter 700) controls the titles which are used within union sound houses. Each particular role on a sound team is segmented into specific job titles such as supervising sound editor (the person who oversees all other members of the team and advances an overall creative concept for the project’s sound), dialogue editor, sound effects editor, foley editor, foley mixer, foley walker, recordist, etc. Ordinarily, a person’s film/TV credit will match his or her job title on a project. However, there are several reasons why the title Sound Designer may be used in credits in lieu of these standard union titles.
One reason may be the traditional use of the term as it was established by Coppola and Murch: the individual has overseen all sound team members and has had an active, creative role in concepts that contributed to the storytelling of the film. In this way, someone is given special commendation by the use of the title Sound Designer rather than Supervising Sound Editor. In essence, they mean the same thing in terms of responsibility. But, Sound Designer has a connotation of creative respect. Another reason would be that the individual played multiple roles in the project (such as supervising sound editor and mixer), and as the term sound designer is outside the purview of the union, this can a convenient way to credit such a person. Keep in mind that in any large studio or union house, an individual may be credited as Sound Designer, but his or her official job title will be one of the union-specified roles. Thus, sound designer is a colloquial term of respect and reverence toward the creative aspect of the work, but it is not an actual job.
Video Games
In interactive and immersive media (video games, VR, etc.), the title of Sound Designer is often used as a catch-all title for each member on the sound team. In general, there will be a bevy of sound designers on each project, who are lead by the Audio Lead. This person, in turn, is supervised by the Audio Director who works closely with the game design department. On large projects, sound designers may be specialized in different areas such as technical sound designers who work closely with programmers, or integrators who specialize in fitting sound into the pipeline of the game. They may also specialize in foley, dialogue, or sound effects. However, on small projects, a sound designer may be required to cover all sound jobs as well as understand its technical integration into the media. This use of the term as a broad descriptor of all sound personnel differs greatly from the use in television and film.
Theater
Theater sound design is a very different animal, indeed, and for that reason, I have left its history to this section. Sound design for theater refers to the choice of music and sounds for a stage production, and the subsequent choice, setup, and use of live audio technology to play those sounds during a performance. This implies an intimate familiarity with the work, and a close alliance with the director and possibly playwright to create an overall soundscape that enhances the work.
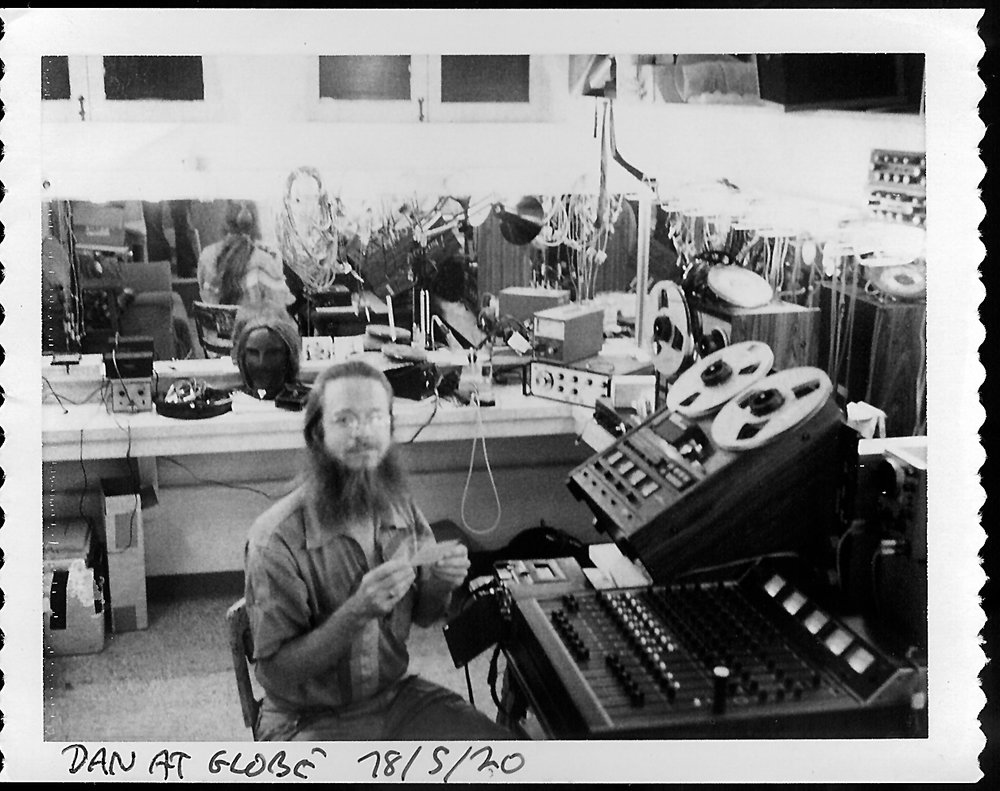
The first use of the term Sound Designer was in the 1968-1969 theatrical season of the American Conservatory Theater and was bestowed upon Dan Dugan who worked three stereo tape decks routed to ten loudspeakers. As technology has advanced over the years and directors have become more accustomed to lush sound design in film and television, this role has become increasingly complex, and in many ways is linked to the role of Sound Artist within the fine arts community.