It feels like technology is developing at an incredible rate with every year that passes, and in the music world, these changes continue to push the boundaries of what is possible for creators as we approach 2020. Several companies specialising in AI music creation have been targeting composers lately, headhunting and recruiting them to develop the technology behind the artificial composition. So who are the AI companies and what do they do?
AIVA
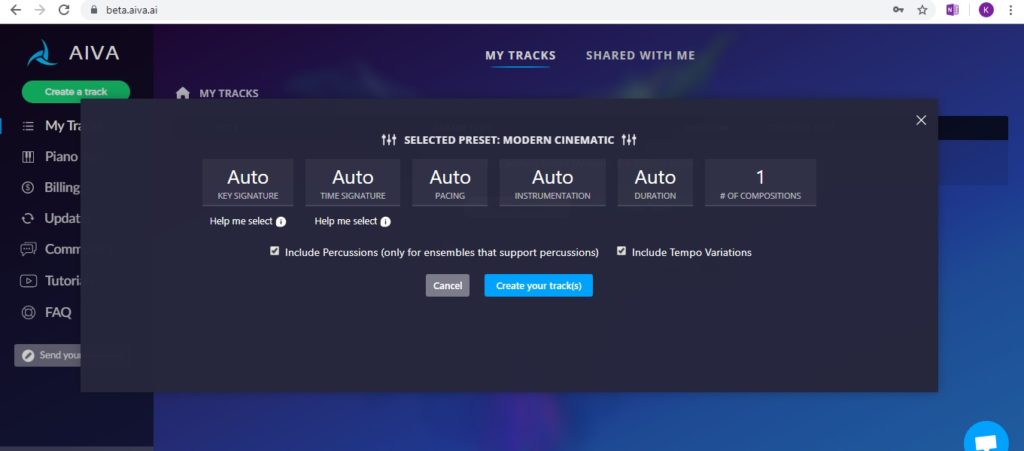
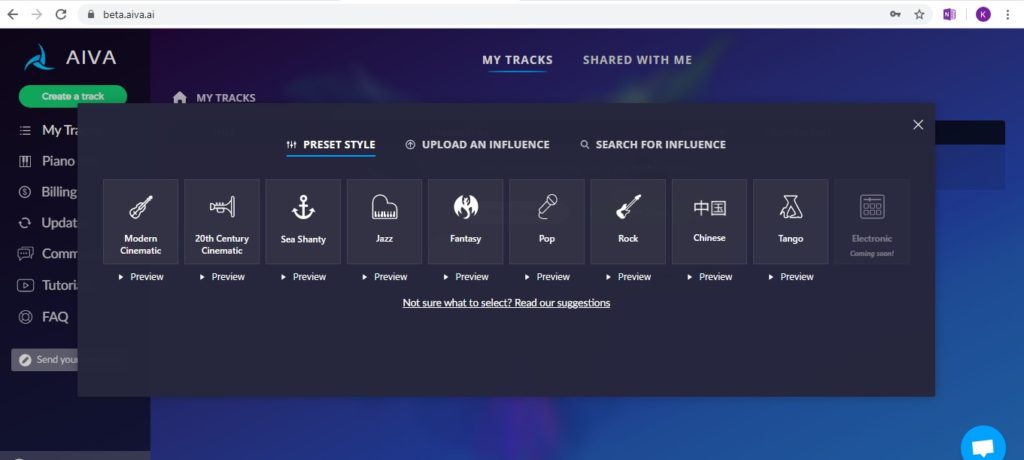
One company called ‘AIVA’ has been the most prevalent that I’ve been aware of this year, and they have reached out to recruit composers stating they are ‘building a platform intended to help composers face the challenges of the creative process’. Their system is based on preset algorithms, simplified and categorised by genre as a starting point.
I set up an account to experiment and found it to be quite different from the demo on the landing page led me to believe. The demo video demonstrates how the user can choose from a major or minor key, instrumentation, and song length to create a new track, and that is it – the piece is created! The playback of the piece has overtones of the keyboard demos of my youth in its overall vibe however I have to admit I am genuinely impressed with the functionality of the melody, harmony, and rhythms as well as the piano roll midi output that is practical for importing into a DAW – it’s really not bad at all.
The magic happens while watching the rest of the demo and seeing how the composer modifies the melody to make slightly more technical sense and sound more thought-out and playable, they shift the voicing and instrumentation of the harmony and add their own contributions to the AI idea. I have to admit that I have similar methods for composing parts when inspiration is thin on the ground, but my methods are not so fast, slick or lengthy and I can completely see the appeal of AIVA being used as a tool for overcoming writers’ block or getting an initial idea that develops quickly.
On the argument against, I was pretty stunned how little input was required from the user to generate the entire piece, which has fundamentally been created by someone else. The biggest musical stumbling block for me was that the melodies sounded obviously computer-generated and a little atonal, not always moving away from the diatonic in the most pleasing ways and transported me back to my lecturing days marking composition and music theory of those learning the fundamentals.
In generating a piece in each of the genres on offer, I generally liked most of the chord progressions and felt this was a high point that would probably be the most useful to me for working speedily, arranging and re-voicing any unconvincing elements with relative ease. While I’m still not 100% sure where I stand morally on the whole thing, my first impressions are that the service is extremely usable, does what it claims to do, and ultimately has been created by composers for those who need help to compose.
Track 1 – https://soundcloud.com/michelle_s-1/aiva-modern-cinematic-eb-minor-strings-brass-110-bpm
Track 2 – https://soundcloud.com/michelle_s-1/aiva-tango-d-major-small-tango-band-90-bpm
Amper
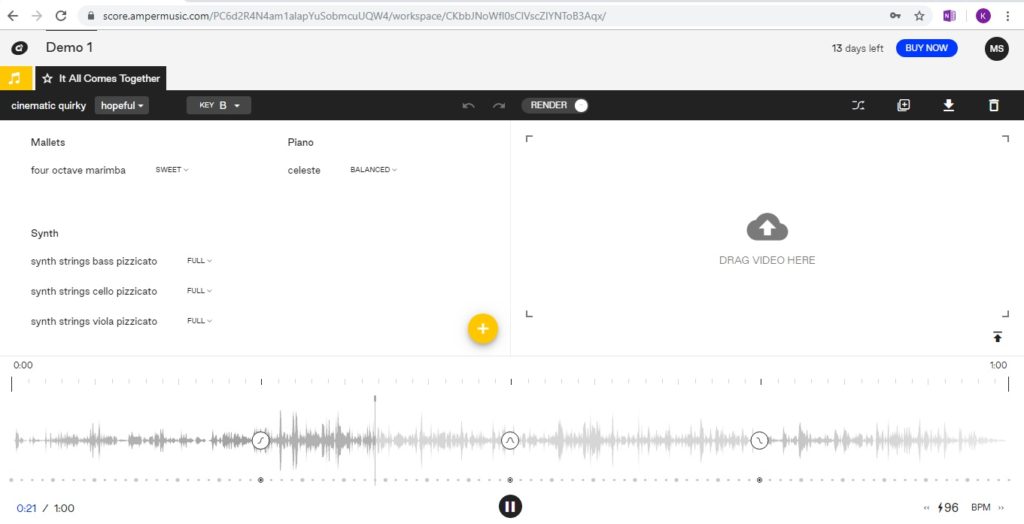
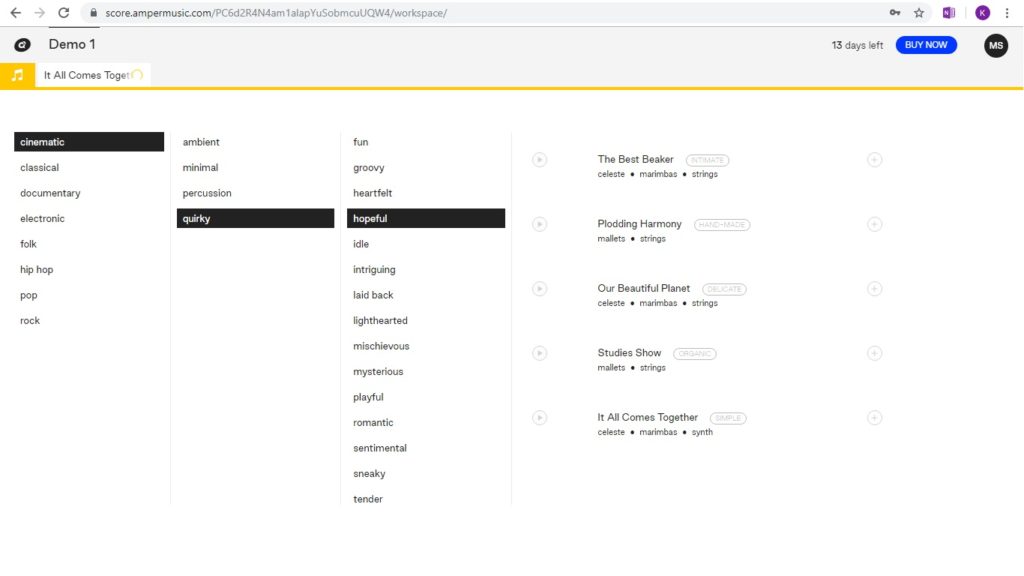
‘Amper’ music is a different yet interesting AI composition site that assists in the creation of music, and the company states that the technology has been taught music theory and how to recognise which music triggers which emotions. The nerd in me disagrees with this concept profusely (the major key ukulele arrangement of ‘Somewhere over the rainbow’ by Israel Kamakawiwo’ole is just one example of why music is far more complex than key and instrumentation assumptions) however in looking at the target market for Amper, this makes far more sense – they provide a service primarily aimed at non-musicians who are faced with the prospect of trawling through reams of library music as a means to support concept such as a corporate video. In a similar vein to AIVA, Amper creates fully-formed ideas to the brief of set parameters such as timing length and tempo with the addition of incorporating a video to the music creation stage, making this a really practical tool for those looking for supporting music. I loaded a piece from the given options and found it to be very usable and accessible to non-musicians. While the price tag to own and use the pieces seems steep, it’s also reassuring that the composers should have been paid a fair fee.
IBM
Similarly, IBM has created compositional AI they have named ‘Watson Beat’ which its creator Janani Mukundan says has been taught how to compose. The website states:
“To teach the system, we broke the music down into its core elements, such as pitch, rhythm, chord progression and instrumentation. We fed a huge number of data points into the neural network and linked them with information on both emotions and musical genres. As a simple example, a ‘spooky’ piece of music will often use an octatonic scale. The idea was to give the system a set of structural reference points so that we would be able to define the kind of music we wanted to hear in natural-language terms. To use Watson Beat, you simply provide up to ten seconds of MIDI music—maybe by plugging in a keyboard and playing a basic melody or set of chords—and tell the system what kind of mood you want the output to sound like. The neural network understands music theory and how emotions are connected to different musical elements, and then it takes your basic ideas and creates something completely new.”
While this poses the same arguments to me as AIVA and Amper with its pros and cons, it’s clearly advertised as a tool to enhance the skills of composers rather than replace them, which is something I appreciated once again and I am curious to see where IBM takes this technology with their consumers in the coming years.
Humtap
The last piece of software I tried myself was an app downloaded onto my phone called ‘Humtap’ which was a slightly different take on AI for music composition. In a lot of ways, this was the least musical of all the software, yet conversely, it was the only one I tried that required something of a live performance – the app works by singing a melody into the phone and choosing the genre. I hummed a simple two-bar melody and played around with the options of what instrument played it back and where the strong beats should fall in the rhythm. The app then creates a harmonic progression around the melody, a separate B section, and this can all loop indefinitely. It’s really easy to experiment, undo, redo, and intuitively create short tracks of electronic, diatonic sounding music. This app by its nature seems like it’s aimed at young people, and I felt that was pretty positive – if Humtap works as a gateway app in getting youngsters interested in creating music using technology at home, then that’s a win from me.
There’s always a discussion to be had around the role of AI in music composition, and I suspect everyone will have a slightly different opinion on where they stand. Some fear the machines will take over and replace humans, others make the argument that this kind of technology will mean everybody will have to work faster because of it, and there are some who fear it will open up the market to less able composers at the mid and lower end of the scale. On the other side, we have to accept that we all crave new, better sounds and sample libraries to work with, and that the development of technology within music has been responsible for much of the good we can all universally agree has happened through the last 5 decades. My lasting impression in researching and experimenting with some of these available AI tools is that they are useful assets to composers but they are simply not capable of the same things as a live composer. To me, emotion cannot be conveyed in the same way because it needs to be felt by the creator and ultimately, music composition is far more complex and meaningful than algorithms and convention.