How TikTok Makes A Grammy Nominee
While social media has already been a fruitful avenue for music promotion, the app TikTok has brought new methods of music promotion to the music scene. On TikTok, artists can release one-minute-long clips of their music on the app, in a format that users can attach to their videos. The ability for the public to have easy access to edited sound files has created a social media space where songs can be shared quickly and widely through mass amounts of people.
This new development of music spread has led artists to market their songs into TikTok trends, as a way of expanding the use of their songs as a TikTok sound file. While there are multiple ways for these sound bites to turn into trends, there are two standout ways that songs turn into trends, to further explore how these trends work, I have laid examples of these two trends through a few of this year’s Grammy-nominated “Album of the Year” artist’s songs files on TikTok.
Dance Trend
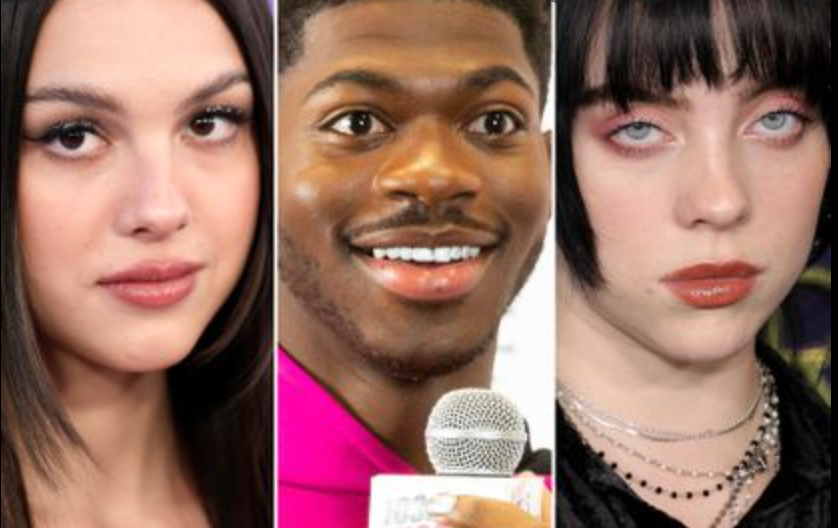
Doja Cat is a prime example of how a dance trend led to her streaming numbers being boosted. In early 2020 her song “Say So” became a popular TikTok sound as it had a dance attached to it. As more people engaged with the mass amount of dance videos using the 30 second sound clip of her song, more people added the song to their playlist. Due to this her “Pink” album jumped on the charts. She continued to use her popularity of dance trends with her songs by creating dances for songs on her next album. On her 2022 Grammy-nominated album, four of the songs have TikTok dance trends. While the Grammy’s are not nominating dance trends, the dance trends are boosting the songs to the Recording Academy’s attention.
Lil Nas X also was able to gain mass attention with his songs by creating a dance trend. For his song, “THAT’S WHAT I WANT”, a dance trend became popularized. This pushed his song to be popular on TikTok. UT is not surprising that his most popular song on Spotify is this song, seeing its popularity and placement on top trends on TikTok.
By using dance trends, clips of songs can gain mass viewership and interest. Doja Cat and Lil Nas X are just two examples of how a good sound clip and dance can make a song successful on the popular charts.
Personal Story Trend
Olivia Rodrigo has taken the world by storm with her debut album “SOUR”. Over half the songs on the album have over 20k videos with the song. However, her song “Traitor” has 20k videos. The main use for the song is to be the background to a personal story. The song adds the element of betrayal to stories of failed relationships or friendships that a user is trying to explain. The use of the song in the videos functions as if it is a part of a movie soundtrack of someone’s life. Through the carefully curated choice of the part of the song to clip for TikTok, Rodrigo was able to connect her song to people in an intimate and personal way. The use of this storytelling in TikTok videos allowed for mass groups of people to connect to the song, thus adding the song to their playlist. Through this chart-topping success, much of which came from her TikTok video popularity, Rodrigo was able to have her debut album nominated for album of the year at the Grammy.
Billie Eilish also had one of her songs be used to tell a story on TikTok. Many users have used “getting Older” to talk about various ways they have grown up, and experiences they went through. The sound has over 500k views. She also has “Happier than Ever”, which was used for the user’s storytelling. In this case, it was for recount breakups that had happened.
Both of these show how songs can become popular on TikTok if they help a user tell a story. Music is meant to tell a story, one that often is intended to connect with the masses. TikTok shows that if the music does a good job of connecting with other stories, then it can become a viral TikTok sound, thus leading to rising to the top of music charts.
The convenience of any user being able to use a sound snippet without having to do their sound editing leads to the easier ability for a sound to become viral, and thus boost an artist’s reach. By simply pressing a button, any user can play an artist’s sound and clip all their followers. Artists and their teams are recognizing how their song trending on TikTok can boost a song to chart-topping status. As we continue to have more social media music marketing avenues emerge, it is important to understand the power they have on an artist’s chart success.