Choosing Software
There are many ways to control show cues on various programmes, and exactly which programmes used are entirely dependent on what the show’s needs are.
My upcoming show in RADA is proving to be a show that has much more than just a standard Qlab and a few microphones; I’ll also be composing for the show, but the composition is very much in fitting with the almost experimental and ‘found sound’ element of said show. It’s set simultaneously in 1882 and 2011, and there should be a ‘Stomp’-esque soundtrack that is driven by the sound, music, and choreography. This presents various challenges, and one of them initially has been deciding what to run the show on. Naturally, I’ll be using Qlab as the main brains of the show. However, Ableton Live will be utilized as well as live mixing.
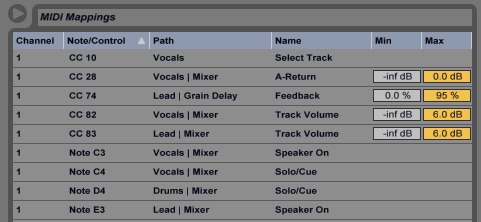
Qlab is incredibly versatile, and as I’ve mentioned in previous posts, it can deal with OSC and MIDI incredibly well. In terms of advanced programming, you can get super specific and create your own set of commands and macros that will do whatever you need it to do, and quickly. Rich Walsh has a fantastic set of downloadable scripts and macros to use with Qlab that can all be found on a Qlab Google Group . Mic Pool has the most definitive Qlab Cookbook that can also be found here (as with OSC and MIDI, you will need a Qlab Pro Audio license to access these features which can be purchased daily, monthly, or annually on the Figure 53 website).
To get Qlab to talk to Ableton is relatively straightforward – again, it’s all MIDI and specifically Control Change. MIDI is incredibly useful in that per channel, we can achieve 128 commands, and each channel (which is up to 8 output devices in Qlab V3) can be partitioned off for separate cues (i.e. Channel 1 might go to Ableton, Channel 2 might go to Lighting, 3 might be Video, and so on). Couple the Control Change with both Ableton’s MIDI Input Ports and its MIDI Map Mode, and you’re on your way to starting to control Ableton via Qlab. Things can get as specific as fade up/down over certain times, fade back up over certain times, stop cues, start loops, and generally control Ableton as if you were live mixing it yourself. The only thing to be wary of at this stage is to ensure that all levels in Ableton are set back to 0db with a separate MIDI cue once desired fades, etc. are completed – Ableton will only be as intelligent as it needs to be!
Using both macros/scripts and sending MIDI cues to Ableton are all features that I will cover in a separate post, only because they deserve their own post to understand all of the features.
So Ableton can do a lot, regarding controlling a show, and it does give us the flexibility to work, but artistically it also opens up a whole new world of opportunity. In RADA we are fortunate enough to own several Ableton Push 2’s, and they’ve very quickly become my new favourite toy! Push is useful as a sampler at its core, but there is so much flexibility that will be incredibly helpful during this next show. I can create loops, edit times, effects, sample rates, and can load any plugins simply; for me, it’s completely changed the live theatre game. I can react in real-time in the rehearsal room based on the choreography and can load new sounds from a whole suite of instruments and drum packs.
I’ll let Ableton themselves tell you more about the Push and what it can do – I’ve only recently started to use Ableton, so it’s as much as voyage of discovery for me, as I’m sure it is for you! More can be read on their website.
I primarily also use Pro Tools for editing any SFX and dialogue; this is because it’s a programme I’ve come to know very well and find that it is dynamic enough for what I need to do. I can again, load plugins quickly, it’s versatile and can load hundreds of tracks, and can talk to external hardware simply (such as the Avid Artist Control which we have in RADA’s main recording studio).
I also sometimes use Logic Pro as well, although I would only use this for music editing. This is because I prefer its ability to quickly load time signatures and is elastic enough that whenever a new track is loaded, it quickly adapts to the time signature on imported audio, and often comes pre-loaded with a vast amount of samples and plugins as standard.
With Ableton edging its way in, however, I might just have to choose a favourite soon because for me Ableton can often provide more realistic sounds, greater flexibility in drag-and-drop (wildly editable) plugins, auto-looping, and can be easily controlled in a live setting.
Often with software though, as with hardware, it’s more about what the sound designer or musician is comfortable with using and what the desired outcome is for the show.